World Of Controls understands the criticality of your requirement and works towards reducing the lead time as much as possible.
DS3800HLXA - High-Speed Data Link Board is available in stock which ships the same day.
DS3800HLXA - High-Speed Data Link Board comes in UNUSED as well as REBUILT condition.
To avail our best deals for DS3800HLXA - High-Speed Data Link Board, contact us and we will get back to you within 24 hours.
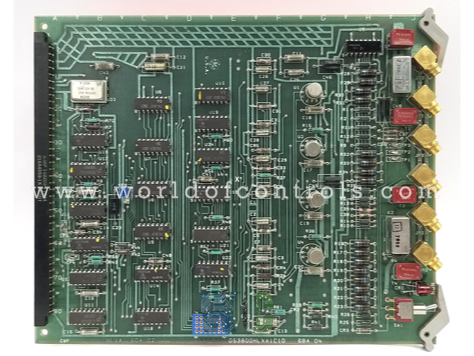
Part Number: DS3800HLXA
Manufacturer: General Electric
Series: Mark IV
Product type: High-Speed Data Link Board
Availability: In Stock
Repair: 3-5 Days
Country of Manufacture: United States (USA)
DS3800HLXA is a high-speed data link board developed by GE. It is a part of Mark IV control system. The board has six connectors for fiber optic cables. It also has a single run-designated red LED indicator. A high-speed data link board, also known as a data communication board or data link interface board, is an electronic component used to facilitate fast and efficient data transfer between different devices or systems. The main purpose of a high-speed data link board is to provide a reliable and high-bandwidth pathway for transmitting data between devices at accelerated rates. They typically incorporate specialized hardware components and advanced communication protocols to achieve this objective.
WOC is happy to assist you with any of your GE requirements. Please contact us by phone or email for pricing and availability on any parts and repairs.
What is DS3800HLXA?
It is a high-speed data link board developed by GE.
How are solenoids and other external devices driven in the system?
Solenoids and other external devices are driven by contacts from relays installed in relay modules. The relay driver module (RDM) contains the relay driver circuits, which control the relays that drive the external devices.
What are the two types of relay driver circuits?
The two types of relay driver circuits are voting and non-voting.
What is the difference between voting and non-voting relay driver circuits?
Voting relay driver circuits require agreement from a majority of input signals to activate the output signal, whereas non-voting relay driver circuits require only a single input signal to activate the output signal.